Truth is defined as that which is true or in accordance with fact or reality and yet it continues to remain elusive. The pursuit of truth often ends when:
- Preconceptions are confirmed: Intuition and experience are crucial towards evaluating information but are just as often constraints. Unfortunately the truth does not always
 confirm our preferences.
confirm our preferences.
- Preconceptions are confirmed: Intuition and experience are crucial towards evaluating information but are just as often constraints. Unfortunately the truth does not always
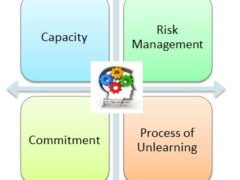
- Rewards outweighs risk: Risk thresholds influence whether or not truth is accessible, if it can be implemented, or if the necessary framework supports are in place to learn from it. Truth often requires significant changes.
- Commitment is outstripped by capacity: Leveraging truth to support innovation requires preexisting skills, competencies, tools, and structures. The process of leveraging truth requires ongoing learning and the organic processes to support them.
Exploring facts and reality is more complicated than the normative values and reductive models we are accustomed to working with. True innovation is often discontinuous and requires jumping from one insight, or creation, to the next. The next step may be completely unrelated from previous insights.
The business scorecard focuses on four domains that can be used to evaluate, drive, and leverage information across the business model ecosystem:
- Financial Metrics emphasize measures that help evaluate allocation, growth, and utilization of monetary resources.
- Customer Metrics emphasize retention, turnover, and satisfaction measures.
- Process Metrics emphasize efficiency, waste, error rates, time, and frequency measures (to name a few).
- People Metrics emphasize learning, training, satisfaction, retention, turnover, and leadership measures.
| Goals | Metrics | Outcome | |
| Financial | |||
| Customer | |||
| Process | |||
| People | |||
Additional insights can be applied across the business model ecosystem when reviewing the following questions:
- What insight does these metrics offer regarding the business model?
- Product/ service offerings?
- Customer retention?
- Process efficiencies?
- Relationships and inter-dependencies?
Although not all innovations represent industry disruption the internal changes required can be felt as quite disruptive to stakeholders and employees.

Innovation requires change. This includes changes to processes, strategies, tools, as well as changes to how existing problems are resolved. Embracing innovation requires a supporting business model in order to ensure the necessary reinforcement, structure, and authority is available.
Without an adequate foundation the efforts to support innovation will likely lose momentum as conflicting priorities, perceptions, and values surface. Resistance is considered inevitable in the process of change but with an appropriate foundation the path to move forward becomes easier.
How is your team supporting innovation? What tools are considered crucial? Share your insights below.
Travis Barker, MPA GCPM
Innovate Vancouver
Innovate Vancouver is a business development & consulting service and technology startup located in Vancouver, BC. Contact Innovate Vancouver to help with your new project. Innovate Vancouver also gives back to the community through business consulting services. Contact us for more details.